ESP Performance Enhancement at Coal-Fired Power Plant in Indonesia
Application
Industry: Power
Capacity: 2 units x100 Megawatts
ESP OEM / Information: Walther
Process: Power Boiler
Country: Sumatera, Indonesia
Problem
The plant’s ESP had been operating for more than 20 years since 1996. Air pollution from the power plant stirred up protest in the neighborhood. It was believed that the cause was due to aging and deterioration of equipment and one of them was Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP) system. Damaged Collecting Plate (CP), rapping system failure, eroded Gas Distribution Screen (GD Screen), and slack Discharge Electrode (DE) were reported to be the major causes of inefficient ESP performance. Rehabilitation of ESP internal parts had been proposed to recover the ESP performance back to its original design capability. However, the plant not only demanded for rehabilitation of the ESP but also ESP performance upgrade.
Solution
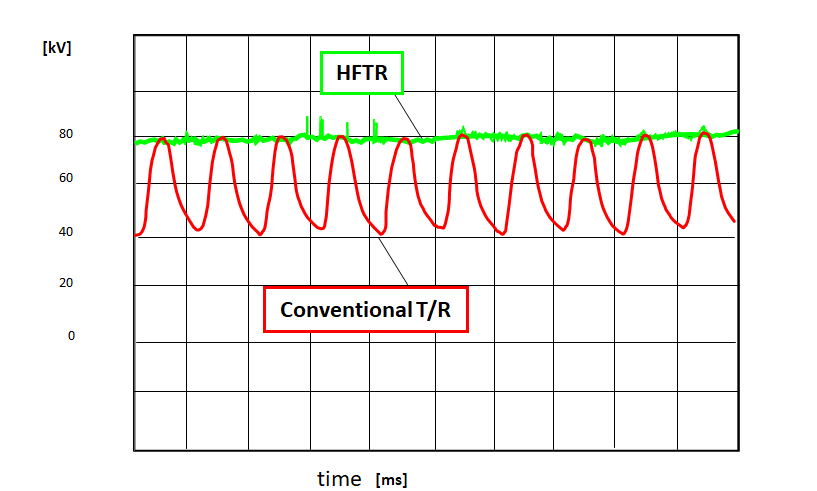
One of the methods to upgrade ESP performance was having an additional field. Additional field means additional collecting area, thus, the capacity of ESP to capture particulate increases. Unfortunately, no extra space was available for an additional field. Still, meeting the plant’s expectation was mandatory. As a result, Rigid Discharge Electrode (RDE) and High Frequency Transformer Rectifier (HFTR) retrofit were proposed. Rehabilitation and upgrade of the ESP unit 1 was completed at the end of 2019 whereas unit 2 retrofit is scheduled to be executed in 2020.
| Old Design | New Design | |
| Collecting Electrode (CE) | Sigma III, 480mm width | C480, 480 mm width |
| Discharge Electrode (DE) | Saw Band DE | RDE |
| Power supply | Conventional T/R
Input: 380V/187.6A, single-phase Output: 96kV/750mA |
HFTR
Input: 400V/136A, 3-phase Output: 83kV/1010mA |
| Sonic Horn | Not Available | 12 sets of sonic horn at rooftop
6 sets of sonic horn at hopper |






Benefit
The condition of the ESP before retrofit was deteriorated due to aging and caused thick dust emission. Rehabilitation and upgrade by replacing internal mechanical parts as well as retrofitting RDE and HFTR have been proven to enhance ESP performance. ESP efficiency significantly increased from 90.6% to 99.1% despite almost 2 times higher the inlet particulate volume than before the retrofit. The discrepancy of boiler load before and after the retrofit was only 3 Megawatts; however the ESP had treated a lot more particulate loading during after-retrofit test. It might have been due to certain process problems that resulted in different inlet particulate content. Outlet particulate emission remarkably reduced from 718.4 mg/Nm3 to 120.75 mg/Nm3 – an 83% improvement. The table below shows detailed emission test data before and after the retrofit:
| Load (MW) | Inlet Particulate (mg/Nm3) @ 7% O2 | Outlet Particulate (mg/Nm3) @ 7% O2 | ESP Efficiency (%) | |
| Before retrofit | 74.5 | 7659.55 | 718.4 | 90.6 |
| After retrofit | 77.5 | 13146.25 | 120.75 | 99.1 |